Management SELinux on Centos/RedHat
Management SELinux on CentOS/RedHat
How to management SELinux on CentOS/RedHat
SELinux (Security Enhanced Linux) is a Linux kernel security module that allows administrators and users more control over access controls. It allows access based on SELinux policy rules.
SELinux policy rules specify how processes and users interact with each other as well as how processes and users interact with files.
When no SELinux policy rule explicitly allows access, such as for a process opening a file, access is denied.
SELinux has three modes:
Enforcing: SELinux allows access based on SELinux policy rules.
Permissive: SELinux only logs actions that would have been denied if running in enforcing mode.
Disabled: No SELinux policy is loaded.
By default, in CentOS, RedHat >= 4, SELinux is enabled and in enforcing mode.
It is recommended to keep SELinux in enforcing mode, but in some cases, you may need to set it to a permissive mode or disable it completely.
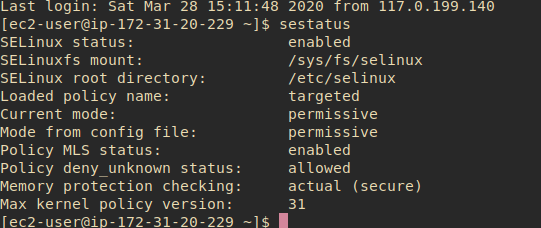
1, Check status SEL
sudo sestatus
2, Change status SELinux
sudo vim /etc/selinux/config
Open file and set the SELINUX mod:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
3, Restart system for update configuration
sudo reboot
Read more info: https://wiki.centos.org/HowTos/SELinux
That's all






Post a Comment